Who were the Romans?
The Romans lived over 2,000 years ago, so how do we know so much about them?
Much of the information we have about the Romans comes from books and diaries that were written at the time. In addition, archaeologists - people who dig in the soil to find ancient things to help us better understand history – have found many ruins and artefacts that the Romans left behind.
These include:
- dishes and bowls
- jewellery
- household decorations
- weapons
- vehicles
- stones
- ruins of houses
The Romans travelled from Italy to Wales to expand the Roman empire.
An empire is new land governed by another country.
The Romans wanted to reign over many other countries and territories and control them from Rome. And this included Britain and Wales.
Video - The Romans
The Romans arrive in Wales
The Romans reached Wales around AD 49.
At the time Wales was inhabited by Celts. The Celts fought hard against the Romans. But after 30 years, the Romans conquered the Celts.
One way the Romans managed to control the Celts was by building Roman forts across the country.
They built one fort in Caernarfon.
The Romans called Caernarfon Segontium. The name of the local Celtic tribe was the Ordovices.

Culture
Food

Ports were important places for the Romans to bring food from abroad into Wales. They also exported Welsh goods to countries overseas.
We know that the Romans liked the following food and drink and brought them to Wales:
- wine
- olive oil
- leeks
- grapes

Dress
How they looked was very important to the Romans. This meant:
- wearing smart clothes
- decorating their houses
- keeping their gardens clean and tidy and using them as places to relax
The Romans liked to wear a toga, and sometimes they would also wear a headdress. A toga was a white garment made from wool that looked like a bed sheet. The Romans wore a toga over a simple tunic.
It was the men who usually wore a toga, although some women did as well.
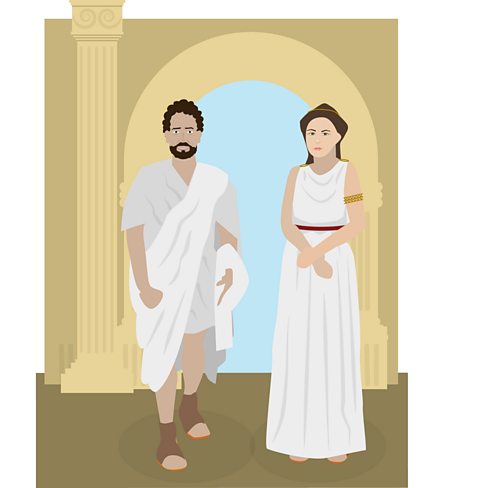

Later, women preferred to wear a stola, a long, pleated dress. A stola could be colourful - red, yellow or blue. Women would tie the dress with a belt, ribbons or ornaments, such as brooches.
Health
The Romans believed that health was very important, and they enjoyed keeping fit, healthy and clean.
In Caerleon today, you can see the remains of the luxurious Roman public bathhouses. There is even a natatio, an outdoor swimming pool.
Keeping fit and health meant that some Romans lived for a long time. A Roman gravestone has been found with the letter C on it. The C stands for the number ‘one hundred’ - which shows how old the person was when they died.
Language
The Romans spoke Latin.
No one speaks Latin today. The language has been dead for centuries. But to this day, Latin’s influence can be seen in many other languages, including Welsh.
Some examples include:
- fossa > ffos (ditch)
- candela > cannwyll (candle)
- liber > llyfr (book)
- ecclesia > eglwys (church)
- stabellum > ystafell (room)
- scola > ysgol (school)
- fenestra > ffenestr (window)
- tristis > trist (sad)
- dolor > dolur (pain)
- pons > pont (bridge)
Leading the way
The Romans were responsible for building infrastructure in Wales. They were very good at building very straight and long roads. Prior to this, Wales had rough tracks full of mud and stones.
The Romans built a road from Caernarfon to Chester. There is also Sarn Helen which runs from Caernarfon to Ceredigion and then east to Brecon.
These long and straight roads were a very effective way of moving soldiers across the country.Excellent roads were among the most important things left behind by the Romans when they left.
Caerleon
One of the Roman roads led into the town of Caerleon in south Wales. Caerleon had an amazing amphitheatre. The amphitheatre could hold nearly 6,000 people. This is where the Roman soldiers watched gladiators fighting each other for entertainment.
These could also be found in Caerleon:
impressive fort
headquarters
market
port
hospital
barns
practice fields

Mosaics
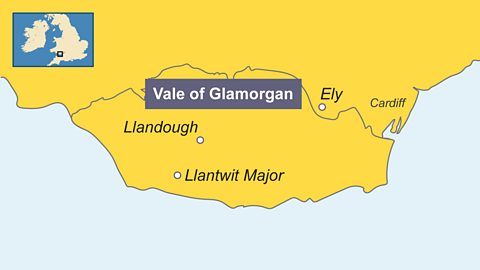
In the Vale of Glamorgan, several large farms and villas were built by wealthy farmers, for example:
Ely
Llandough
Llantwit Major
There, new crops were introduced into Wales, for example:
apples
oats
carrots
leeks
A villa is a large grand house. In these villas there were baths, central heating and characteristic Roman mosaics. A mosaic is a pattern or picture made from small pieces of stone or glass.

The Romans leave Wales
The Romans had probably left Britain by AD 410.
So, after 400 years, the Roman empire was over.
Quiz – True or False?
Maths 8-11
Videos and activities

Welsh Second Language 8-11
Exciting videos and activities for learning Welsh

Sustainability 8-11
A collection of lessons for pupils aged between 8 and 11
